The Need For Oracle Database Replication
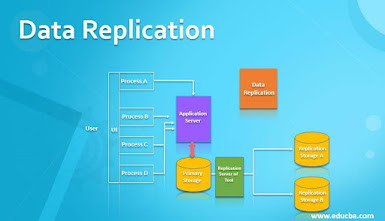
Database replication is the task of storing data in several locations, both local and remote so that the current database can be accessed from any point. Data is replicated from a server to be shared across regions. The main benefit of database replication is disaster recovery. When an outage occurs in the primary server, the secondary servers where data has been replicated are automatically triggered and there is no break in work. After the issue is resolved the primary server is updated with all records that occurred in the break period.
The mechanism that is
greatly used by various organizations to distribute, share
and consolidate their data is Oracle replication. It helps in creating,
distributing, and syncing data over multiple locations so that consolidating
data from various sources and sharing data with users and vendors can be done
easily and seamlessly either globally or locally. The cost of data analytics
with query overload by splitting OLTP and the generation of reports into
various systems is also greatly facilitated by Oracle replication.
Another advantage of Oracle replication is that users can access information whenever
needed by creating synchronized multiple copies of an Oracle database. These
are useful for testing, business reporting, backups for disaster recovery, and
distributed data processing.
There are two forms of Oracle replication.
The first is Synchronous replication where data is
replicated continuously to the primary and secondary areas. The data replicated
remains the same in the source and target databases.
The other is Asynchronous replication where the data
is written first to the primary server and then committed to a secondary source
instead of the two working together. The data is copied at pre-determined
intervals.



Comments
Post a Comment